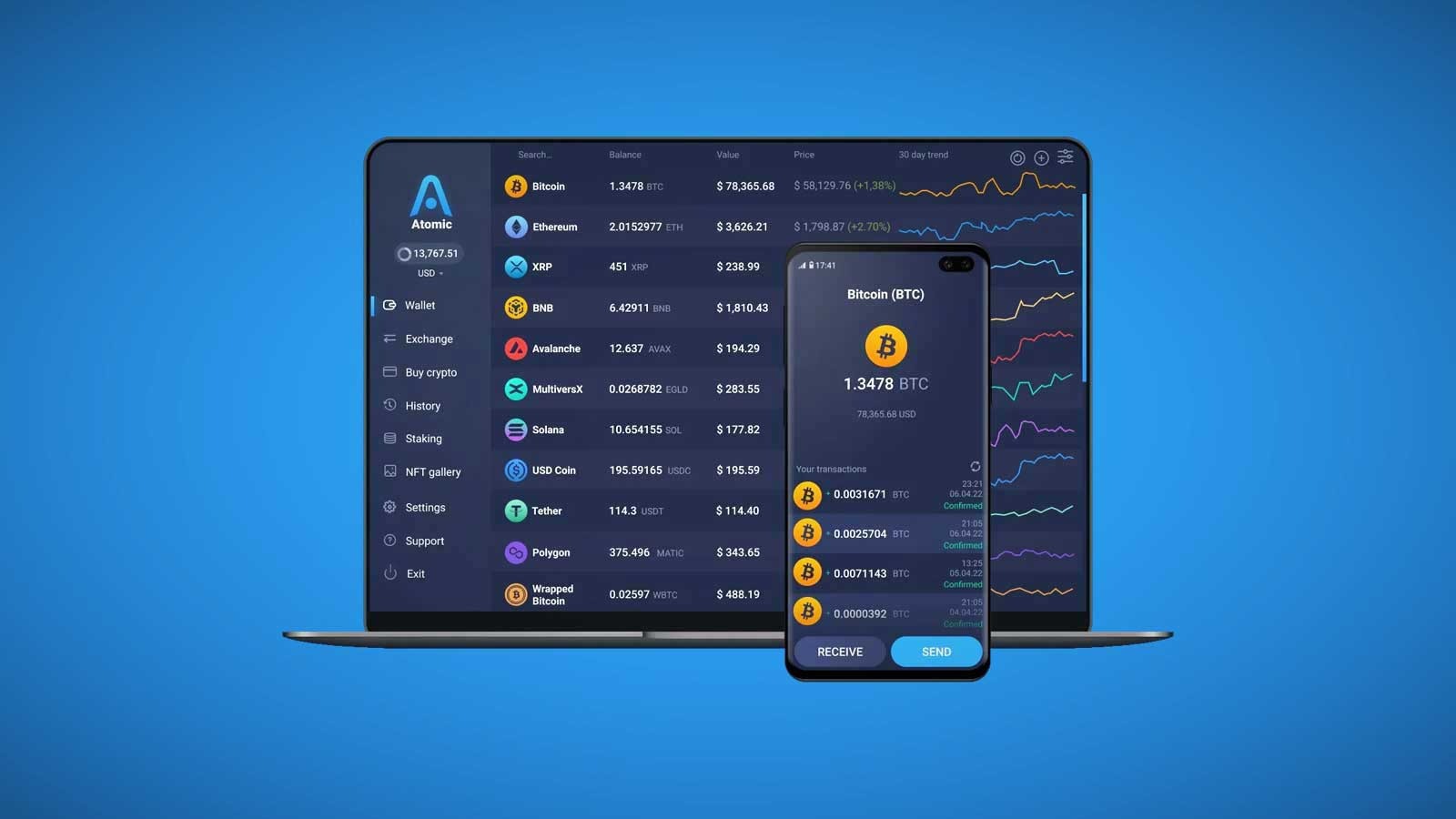
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the way people perceive and handle money. With the rapid adoption of digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others, ensuring the safe storage and management of these assets has become crucial. This is where a crypto Ledger hardware wallet comes into play.
In this article, we’ll explore what crypto wallets are, the different types available, and why they are indispensable for anyone involved in cryptocurrency transactions.
What is a Crypto Wallet?
A crypto wallet is a digital tool that allows users to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies. It does not physically hold digital coins or tokens; instead, it holds the cryptographic keys necessary to interact with blockchain networks. These keys are essential for performing transactions and ensuring ownership of the crypto assets.
Crypto wallets are divided into two main types:
- Private Key: This is the key that enables users to sign transactions and prove ownership of the digital currency. It is highly sensitive and should be kept secure at all times.
- Public Key: This is the address users share with others to receive payments or assets. Think of it as your bank account number.
Types of Crypto Wallets
There are several types of crypto wallets, each with its unique features and levels of security.
1. Hot Wallets (Software Wallets)
Hot wallets are software-based wallets that are connected to the internet. They are convenient and easy to use, making them a popular choice for active traders. However, because they are always online, hot wallets are more vulnerable to hacking and cyberattacks.
Examples of hot wallets include:
- Mobile Wallets: Installed on smartphones, these wallets allow users to store their crypto assets and make transactions on the go.
- Desktop Wallets: These wallets are installed on a personal computer, offering more security than mobile wallets.
- Web Wallets: Hosted on online platforms, these wallets can be accessed from any device with internet connectivity.
2. Cold Wallets (Hardware Wallets)
Cold wallets are offline storage solutions for cryptocurrencies. Since they are not connected to the internet, they are far less vulnerable to hacking, making them a preferred option for long-term storage of large amounts of digital assets. Cold wallets store the private keys on hardware devices.
Examples of cold wallets include:
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices like Ledger and Trezor that securely store private keys offline.
- Paper Wallets: A paper printout containing the public and private keys, typically used for long-term storage.
3. Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets
- Custodial Wallets: These wallets are managed by third-party services (like exchanges or financial institutions), which means the service provider holds the private keys on behalf of the user. While custodial wallets offer convenience, they come with the risk of the service being hacked or the provider going out of business.
- Non-Custodial Wallets: These wallets give the user full control over their private keys. The user is solely responsible for securing and managing their keys, providing a higher level of autonomy and security.
Why Are Crypto Wallets Important?
- Security: The primary function of a crypto wallet is to secure your private keys. The keys are the gateway to your cryptocurrency holdings, and if they are compromised, your assets are at risk. Strong encryption methods are employed in wallets to ensure that your private keys are protected.
- Control: With a non-custodial wallet, you have full control over your crypto assets. This is an appealing feature for those who want to avoid relying on third parties for the security of their funds.
- Transaction Management: Crypto wallets are essential for sending, receiving, and managing digital currencies. Whether you’re making a simple transaction or managing a diversified portfolio, a wallet acts as the interface between you and the blockchain network.
- Anonymity and Privacy: Many crypto wallets prioritize user anonymity. While transactions are recorded on the blockchain, they are pseudonymous. This means that your personal identity is not necessarily tied to your crypto address, offering a degree of privacy.
- Access to DApps and DeFi: With the rise of decentralized applications (DApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi), having a crypto wallet is essential for interacting with these platforms. Many wallets allow users to connect directly with decentralized services for lending, borrowing, staking, and more.
How to Choose the Right Crypto Wallet
When selecting a crypto wallet, there are several factors to consider:
- Security: Make sure the wallet has strong security features, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), multi-signature support, and encryption.
- User-Friendliness: Choose a wallet that is easy to use and supports the cryptocurrencies you wish to store. Some wallets are better suited for beginners, while others offer more advanced features for experienced users.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the wallet is compatible with your preferred devices and operating systems.
- Backup Options: Choose a wallet that offers secure backup options in case you lose access to your private keys.
- Reputation: Do thorough research on the wallet provider to ensure they are reputable and have a history of providing reliable service.